In modern websites and applications, data analysis and tracking user behavior are crucial.
Google Tag Manager (GTM), as a free tool, greatly simplifies the management of tracking codes (or “tags”) in websites and applications. It benefits not only developers but also marketers and data analysts by making it easier to track various user behaviors.
What is Google Tag Manager?
GTM is a Tag Management System (TMS) that allows you to manage and deploy various marketing and analytics tags (such as Google Analytics, Google Ads, etc.) without changing the source code of your website. With GTM, you can add, modify, and remove code snippets (tags) on a unified platform without directly manipulating code.
Core Concepts
Tag:A tag is a code snippet embedded in a webpage or application used to collect and send data. For example, you can create a Google Analytics tag to track page views.
Trigger:A trigger defines the conditions under which a tag fires. For instance, when a user visits a specific page, clicks a button, or submits a form, GTM executes the corresponding tag based on your configured trigger.
Variable:A variable is a placeholder for storing information. It can be a predefined value (such as the URL of the current page) or a custom parameter used in the settings of triggers and tags.
Workspace:Each GTM account contains multiple workspaces, allowing different people to edit different settings simultaneously. In a workspace, you can preview, test, and publish your changes.
Why Use GTM?
No Development Resources Needed:Previously, adding analytics and marketing codes to a website often required the help of developers. With GTM, marketers or analysts can add codes themselves without relying on the development team, significantly improving efficiency.
Centralized Management:GTM allows you to manage all tracking codes from a single dashboard, reducing the scattering of tags throughout the code, which helps avoid conflicts and management chaos.
Quick Updates:Updating or removing a tag through GTM doesn’t require redeploying the website code, which lowers the risk of modifying source code and shortens adjustment time.
Enhanced Debugging Features:GTM provides rich debugging tools to help you see when each tag is triggered, ensuring the code executes correctly.
How to Use GTM?
- Create a GTM Account and Install the Code:First, you need a Google account. Then, log in to the GTM website to create a new GTM container. Next, embed the generated GTM code into your website (usually placed in theandtags).
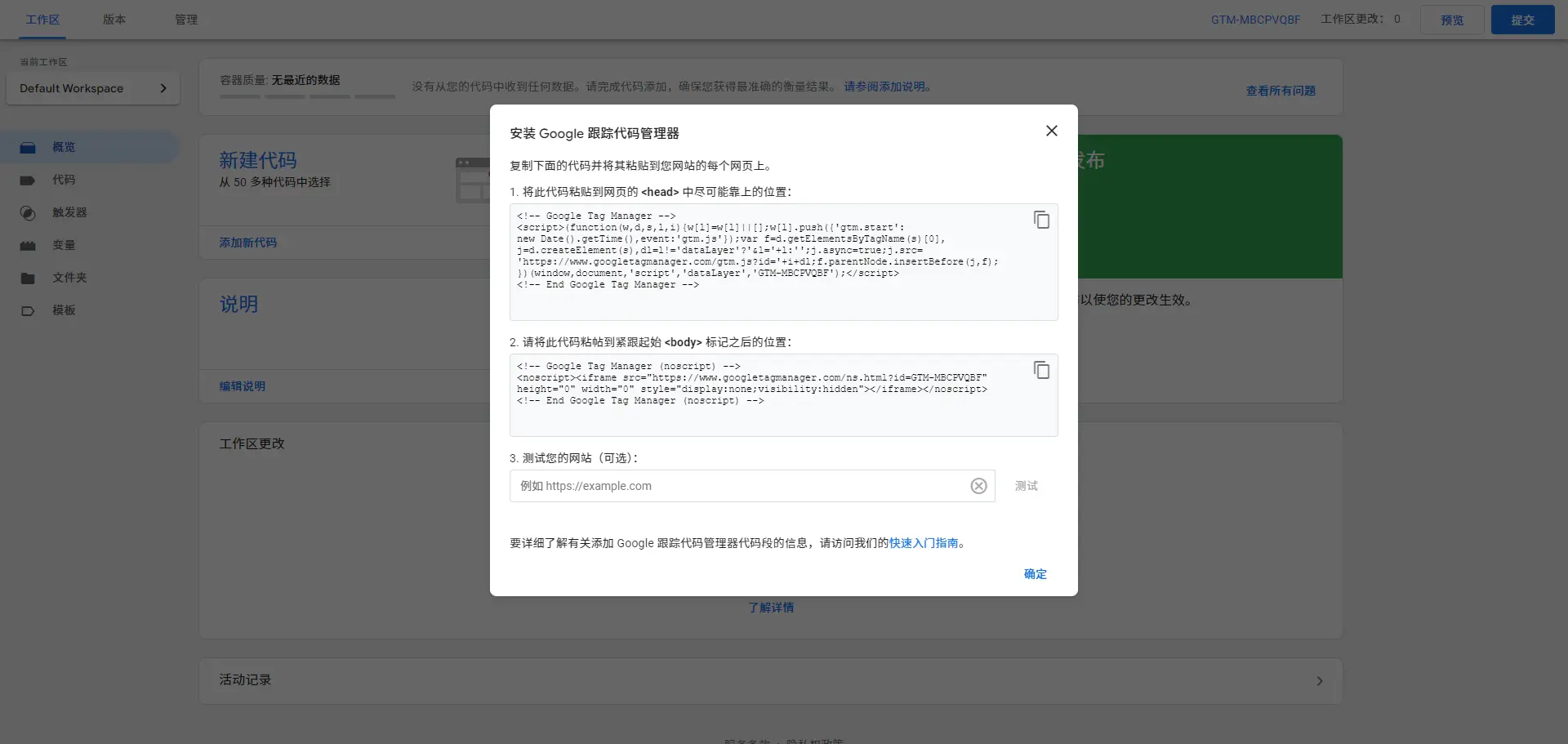
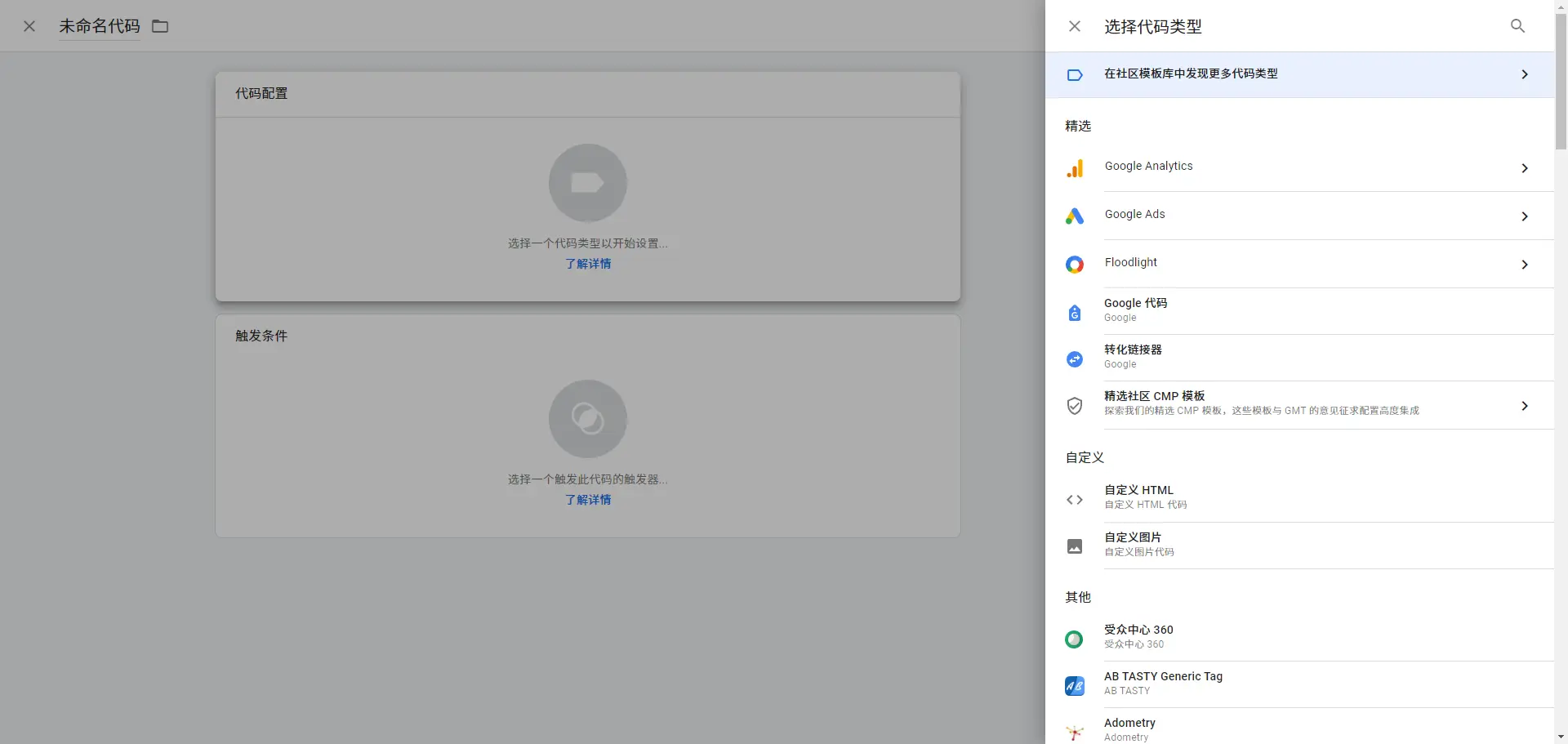
- Add Tags:Based on your needs, add the required tags. For instance, when adding a Google Analytics tag, simply select the preset tag type, enter your Google Analytics tracking ID, and set the trigger (e.g., fire on page load).
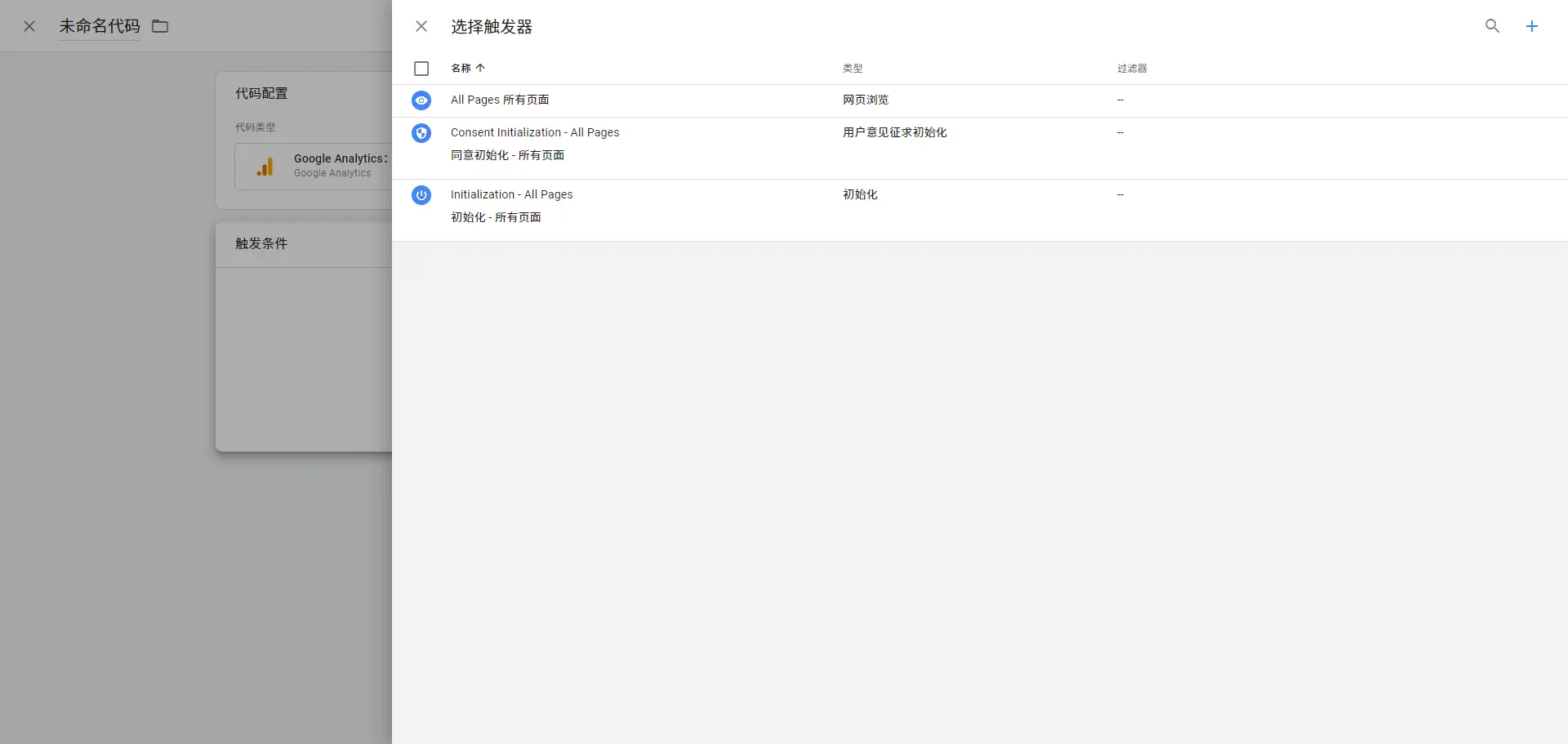
- Set Triggers:Triggers determine when a tag is executed. You can set different trigger conditions, such as page loads, click events, or form submissions.
- Debug and Preview:Before publishing a tag, use GTM’s preview mode to debug your settings and ensure all tags and triggers work as intended.
- Publish:Once everything is confirmed to be working, click the “Submit” button to publish your changes. GTM will automatically apply the new configuration to your website.
Practical Application Scenarios of GTM
Website Traffic Tracking:With GTM, marketers can quickly add or modify Google Analytics codes to track visitor traffic, page dwell time, source channels, and other data.
Advertising Performance Monitoring:GTM allows easy management of tracking codes from multiple advertising platforms, such as Facebook Pixel and Google Ads, to analyze click-through rates and conversion rates.
User Behavior Analysis:In addition to basic page view data, GTM can also track specific user behaviors, such as button clicks, file downloads, and video plays, helping you understand user interaction habits on the website.
Considerations
Privacy and Data Security:When using GTM, ensure compliance with local data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, especially when collecting personal data. You should clearly inform users and obtain consent.
Avoid Excessive Tags:Although GTM allows you to easily add tags, too many tags may affect website performance. Therefore, it’s essential to regularly check and remove unnecessary tags.
Regular Testing and Optimization:Even if tags are set up correctly, regular testing is essential to ensure that tags and triggers remain effective as website content and structure change.
Conclusion
Google Tag Manager is a powerful and flexible tool that not only reduces the workload for technical personnel but also allows non-technical users to manage and monitor website data more freely. By using GTM, you can easily configure and optimize various tag tracking, significantly improving the operational efficiency of your website. If you haven’t started using GTM yet, it’s highly recommended to begin soon, as it will provide significant assistance for your data analysis and marketing strategies.